
Windows Server 2016 and above have build-in the Windows Defender, so the extension will only apply the configuration.īelow we will walk through on how to deploy & manage the Microsoft Antimalware Extension Using the Azure Portal (Single VM), Using the Azure Security Center (Multiple VMs)and Using PowerShell for a Single VMand for Multiple VMs filtered by Resource Groups or Tags. For the 3rd party extensions you need to add your key.įor Windows Server VMs up to version 2012 R2, the extension will install the System Center Endpoint Protection client and apply the configuration policies. Microsoft Antimalware for Azure Virtual Machines is a real-time protection capability that helps identify and remove viruses, spyware, and other malicious software, with configurable alerts when known malicious or unwanted software attempts to install itself or run on your system and it is absolutely free. Azure provides the ability to add an Endpoint Protection Solution to all Azure VMs. There is no need to point out that all VMs must have an Endpoint Protection Solution. Even using PowerShell there is not a single command to manage the Microsoft Antimalware settings.
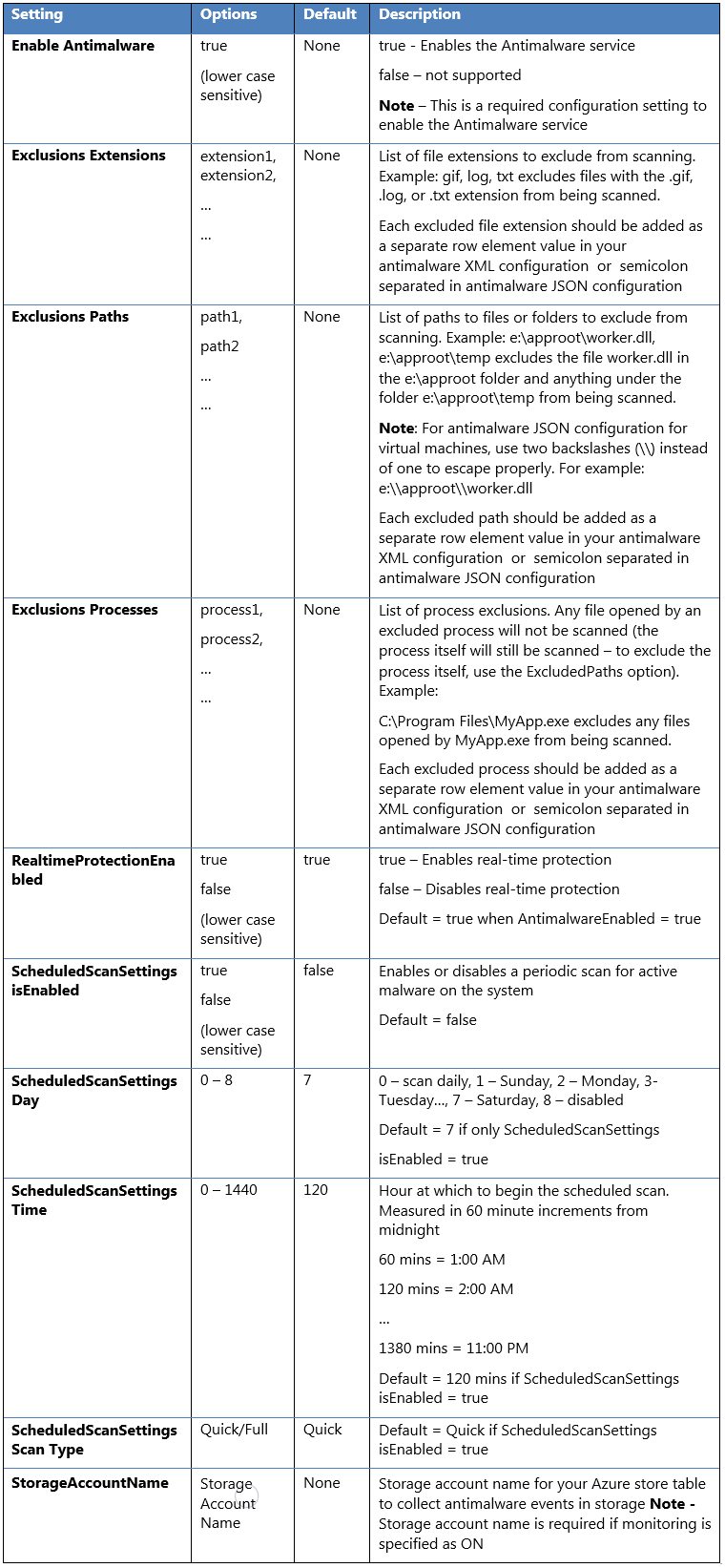
There is no way to manage the Microsoft Antimalware exclusion list and auto-scan setting from the portal or from inside the VM. But after that, the management of the extension is somehow tricky. You can easily enable the Microsoft Antimalware Extension from the Azure Portal upon the Azure VM creation or by using the Extensions blade. Azure VM Antimalware Extension ManagementĪzure VM Antimalware Extension Management has always been a tricky subject.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
